| Polymer |
[Japanese] |
|
|
| Polymer |
In PoLyInfo, information on Polymer is caught at three following levels
and arranged.
- 1. Constitutional repeating unit (CRU) / Constituional unit(CU)
- Level by which Polymer as molecule is discerned from the unit of chemical
structure that composes it. It is especially said, "Constitutional
repeating unit (CRU)" for a regular polymer.
-
- 2. Polymer chain / Polymer molecule
- Level by which one Polymer molecule is discerned as a connected body of
a lot of constitutional units (CU) /constituional repeating units (CRU).
-
- 3. Polymeric material
- Level of material as set of Polymer chain/Polymer molecule.
It uses when saying ..word "Polymer".. the whole in the homepage
and Help of PoLyInfo these, and the corresponding term of 1.-3.
- when of each is distinguished is used. Moreover, 2. and 3. are matched
in 1. and the meaning to make it compare, and it is called, "Polymer
sample".
|
|
| Constitutional repeating unit (CRU) / Constitutional unit (CU) |
-
- constitutional repeating unit (CRU) (in polymers)
The smallest constitutional unit the repetition of which constitutes a regular macromolecule, a regular oligomer molecule, a regular block or a regular chain. 1996, 68, 2291
constitutional unit
An atom or group of atoms (with pendant atoms or groups, if any) comprising
a part of the essential structure of a macromolecule, an oligomer molecule, a block or a chain.
- In PoLyInfo, the unit of the chemical structure that can describe Polymer
chain is called "Constitutional repeating unit/constituional unit".
"Constitutional repeating unit (CRU)" means a minimum unit of
chemical structures that can describe the polymer chain that excludes the
end radical and the joint part by the repetition in the word used only
in case of a regular linear polymer.
"Constitutional unit (CU)" means the unit of a constant chemical
structure that can describe polymer chain/polymer molecule by the repetition
and the combination in the word used regardless of the kind of Polymer,
which contain the end radical and the joint part.
Constitutional repeating unit (CRU) / Constituional unit (CU) is targeted
in discernment and identification in the polymer dictionary in PoLyInfo.
Moreover, it expresses it bringing these together in the word of "Constitutional
unit" or "CU".
|
|
|
Polymer dictionary |
|
Polymer dictionary is a compound registry system only for polymer developed by PoLyInfo. Identification of the chemical
structure is done based on the chemical structure of constituional repeating unit (CRU).
It is identified, by the function of the polymer dictionary based on the
chemical structure of the constituional unit, and an original identification
number (Polymer ID) is given to Polymer collected in PoLyInfo.
The following item that can be decided from the chemical structure of the
constituional unit is collected in the polymer dictionary.
The following item of each sample that adopts data used to identify the
polymer is collected.
Moreover, information on the monomers that are the raw material of the
polymer is related to the polymer dictionary, and collected in monomer
information.
- Reference document concerning polymer dictionary
The 21th informationization study round-table discussion lecture summary
collection, 82(1998)
- Reference document concerning whole of PoLyInfo
Informatics symposium lecture thesis collection in 2000, 41(2000)
|
|
Compound registry system |
|
Compound registry system is a computer system that identifies the compound.
Centering on the chemical structure data expressed with the form of computer
readable, data, such as various kinds of names and a molecular formula,
is matched and recorded. Since discernment and identification of the data
recorded are done based on chemical structure and it is managed unitary,
it can prevent duplicated registration of the same compound.
Moreover, the user can search the specified compound from either the name
or the chemical structure by using the compound registry system.
There are typical compound registry systems by Chemical Abstracts Service(CAS)
and a Japanese compound dictionary system by JST, etc.
|
|
|
Polymer ID |
|
Unique management number given after polymer is identified by function
of polymer dictionary based on chemical structure of constituional unit. Polymer ID is made in the form of abbreviation P that show Polymer +
of six digits numerical value (ex. P150045). |
|
Sample ID |
|
Data identification number of each Polymer sample. This number is truly unique in PoLyInfo.The number is shown as a reference
number and a polymer sequence number in the reference. |
|
Polymer names |
|
Because data is arranged at constituional unit (CU) level and polymeric material (sample) level in PoLyInfo, the names are
shown as the CU name and the material name, and the following Polymer names
of the kind of are collected. The polymers are named in accordance with
the IUPAC nomenclature rules or recommendations.
|
|
Structure based name
Because data is arranged at constituional unit (CU) level and polymeric
material (sample) level in PoLyInfo, the names are shown as the CU name
and the material name, and the following Polymer names of the kind of are
collected. The polymers are named in accordance with the IUPAC nomenclature
rules or recommendations.
| ex.) |
PET: -O-(CH2)2-O-CO-{pC6}-CO- |
poly(oxyethyleneoxyterephthaloyl) |
|
PMMA: -CH(CH3)(COOCH3)-CH2- |
poly(1-methoxycarbonyl-1-methylethylene) |
|
Source based name
Name based on raw material (monomer) used for polymerization.
The monomer name is described after prefix poly directly(one word name),
or enclosed in curves, square brackets, or braces. The monomer names used
are in accordance with the organic compound nomenclature of IUPAC 93.
| ex.) |
poly(ethylene terephthalate), poly(methyl methacrylate) |
|
Trivial name
The name that clearly corresponds to a specific chemical structure is collected
as a trivial name by the name used in general excluding the structure-based
name and the source-based name.
However, the trivial name to which the chemical structure cannot be fixed
is collected to the generic name.
| ex.) |
nylon 6,6, polyacetaldehyde |
|
Abbreviation
Brief expression to structure-based name, source-based name, and CRU/CU
trivial names. For instance, it is abbreviation that "Poly styrene"
places the initial of the name in a line like "PS" and is named.
|
Generic name
Name expressed bringing polymer with common unit of composition (repetition)
together. It is the one that the Polymer classification specified with
JST was subdivided further.
|
Trade Name
Name of polymeric material sold as material. When the brand name is shown
in the document etc. , the one with a clear range of Polymer that corresponds
adopts this.
The sign that shows that it is a trademark such as NameTM (registration) is not included in the name.
|
Generic Name
In the name that catches features of the structure and property etc. of
the polymeric material, it is name corresponding to the two or more kind
of polymeric material.
| ex.) |
liquid crystalline polymer |
|
Trivial Name
Name that catches polymeric material, Polymer set, and features of structure
and property etc. of Polymer chain and the brief expression. The one corresponding
to specific and the unit and making clear the composition (repetition)
is adopted.
| ex.) |
high density polyethylene, it-PS |
|
|
|
Representative name of polymer |
|
Although there are various kinds of polymer names, such as a structure-based
name, a source-based name, and a trivial name, the name considered to be
used best in it is made into the "polymer representation name."
Which name is representative Polymer name has been selected in the following
order from among the name (name given to constituional unit (CU)) that differs in each Polymer, and is registered in the polymer dictionary.
- 1. Source-based name
(However, the trivial name of the nylon is assumed to be representative Polymer name by priority when there is a source-based name.)
-
- 2. Trivial name
-
- 3. Structure-based name
|
|
Polymer classification |
|
The polymers are classified into 22 kinds based on the chemical structure
of constituional unit (CU) of polymer as follows. "Aliphatic hydrocarbon" and "Aromatic
ring" under Definition have reflected the content shown in the following.
- Aliphatic hydrocarbon
acyclic hydrocarbons and cyclic hydrocarbons except aromatic series( the
unsaturated bond can be included. )
- Aromatic ring
Aromatic polycyclic hydrocarbons (example naphthalene), aromatic heterocycles
(example pyridine), and these substituent groups.
|
|
01. Polyacrylics
A polymer that consists of the aliphatic hydrocarbon radical, and at least
one of radicals shown in the following is directly connected to the main
chain carbon. (The main chain carbon is shown as *, and there is no limitation
as part #. )
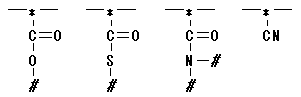
[Remarks]
- The carbon atom of a main chain of prefered constituional unit (CU) is
not limited. (Do not limit the carbon atom of a main chain as two. )
- There can be two radicals or more that characterize polyacrylics.
- Polymer classified into Polyacrylics is classified into Polyvinyls at the
same time.
- It is likely to be classified by the structure at the same time with Polystyrenes.
|
02. Polyamides / thioamides
Polymer including the following partial structures on main chain. (X shows
either of O or S. )
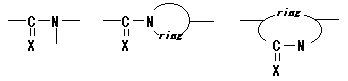
ex.) The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like
the above-mentioned.
However, exclude the following cases.
> N-CO - etc. of Polyurethanes / thiourethanes> N-CO-O-
> N-CO in Polyureas/thioureas > N-CO-N <- etc.
> N-CO of Polyimides/thioimides -CO-N-CO-- etc.
|
03. Polyanhydrides / thioanhydrides
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (Xi shows either of O or S. )
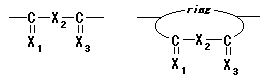
|
04. Polycarbonates / thiocarbonates
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (Xi shows either of O or S. )
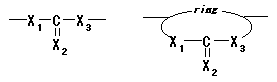
|
05. Polydienes
Polymer that consists of aliphatic hydrocarbon radical and halogen, and
has double bond C=C or one or more triple bonds C≡C on main chain and/or
on side chain. (one that contains one or more unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon
radicals)
[Remarks]
- Polymer including the saturated and/or unsaturated aliphatic cyclic hydrocarbon
radical is included here.
- The one without the aromatic ring is included.
- The one including triple bond C≡C is also included.
|
06. Polyesters / thioesters
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (Xi shows either of O or S. )
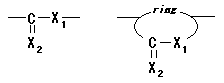
However, exclude the following cases.
- CO-O- etc. of Polyurethanes/thiourethanes > N-CO-O-
- CO-O- etc. of Polyanhydrides/thioanhydrides -CO-O-CO-
- CO-O- etc. of Polycarbonates/thiocarbonates -O-CO-O-
|
07. Polyhalo-olefins
Polymer (Polyolefins) composed only of saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon
radical, from which at least one among hydrogens is substituted for halogen.
[Remarks]
- When the halogen atom is not directly connected to the main chain carbon,
it is included here.
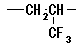
- When the halogen is directly connected to the main chain carbon, it is
likely to be classified into not only Polyhalo-olefins but also Polyvinyls.
|
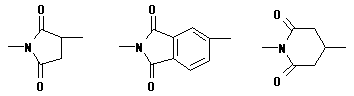
08. Polyimides / thioimides
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (Xi shows either of O or S. )
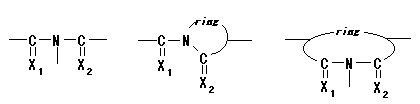
ex.) The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like
the above-mentioned.
 |
09. Polyimines
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain.
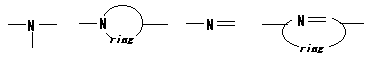
ex.) The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like
the above-mentioned.
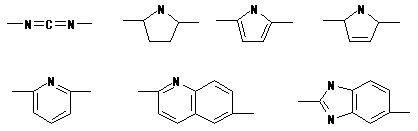
However, exclude the following cases.
-N< etc. in Polyamides/thioamides -CO-N<
-N< etc. in Polyurethanes/thiourethanes >N-CO-O-
-N ..-..< in Polyureas/thioureas >N-CO-N < etc.
-N< etc. in Polyimides/thioimides -CO-N-CO-
-N< etc. in Polysulfones/sulfoxides/sulfonates/sulfoamides -SO2-N<
|
10. Polyketones / thioketones
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (X shows
either of O or S. )
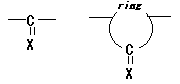
However, exclude the following cases.
- CO- etc. in Polyesters/thioesters -CO-O-
- CO- etc. in Polyamides/thioamides -CO-N <
- CO- etc. in Polyurethanes/thiourethanes >N-CO-O-
- CO- etc. in Polyureas/thioureas >N-CO-N<
- CO- etc. in Polyimides/thioimides -CO-N-CO-
- CO- etc. in Polyanhydrides/thioanhydrides -CO-O-CO-
- CO- etc. in Polycarbonates/thiocarbonates -O-CO-O- |
11. Polyolefins
Polymer composed only of saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical.
[Remarks]
- The one including the unsaturated carbon bond is not included here.
|
12. Polyoxides / ethers/acetals
Polymer contains -O- and/or ring structure including -O- on the main chan.
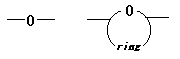
ex.) The followings are examples of partial structures of above-mentioned
polymers.
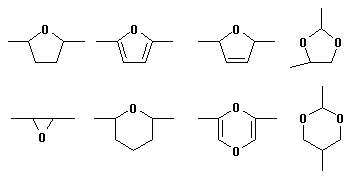
However, exclude the following cases.
-O- etc. in Polyesters/thioesters -CO-O-
-O- etc. of Polyurethanes/thiourethanes >N-CO-O-
-O- etc. of Polyanhydrides/thioanhydrides -CO-O-CO-
-O- etc. of Polycarbonates/thiocarbonates -O-CO-O-
-O- etc. of Polysulfones/sulfoxides/sulfonates/sulfoamides -SO2-O-
[Remarks]
- When -O- that is adjacent to Si on a main chain is contained, it is considered
SiO of the siloxane radical, and doesn't consider O - that characterizes
Polyoxides .
|
13. Polyphenylenes
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (X shows
either of O or S.)
|
14. Polyphosphazenes
Polymer including phosphazene P=N-structures the following on main chain.
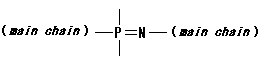 |
15. Polysiloxanes / silanes
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain.
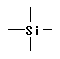 |
16. Polystyrenes
Polymer that consists of the aliphatic hydrocarbon radical, and the aromatic
ring is directly connected to at least one of the main chain carbon inside.
[Remarks]
- Because the carbon atoms of a main chain of constituional unit (CU) is
not limited to two, following polymer is included here.
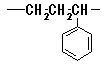
- Polymer classified into Polystyrenes is classified into Polyvinyls at the
same time.
|
17. Polysulfides
Polymer containing -S- or the ring structure including -S- on a main chain.
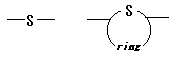
ex.) The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like
the above-mentioned.
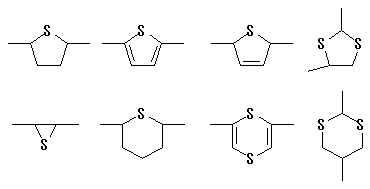
However, exclude the case where it is included in the atomic group where
these partial structures characterize Polymer the following-affiliated.
- S- etc. of Polyester/thioester -CO-S-
- S- etc. of Polyurethanes/thiourethanes > N-CO-S-
- S- etc. of Polyanhydrides/thioanhydrides -CO-S-CO-
- S- etc. of Polycarbonates/thiocarbonates -O-CO-S-
[Remarks]
- S at both ends of Si in a main chain is considered to be S of Polysulfides.
- When the following partial structures are included, it is classified into
Polysulfides and Polyimides.
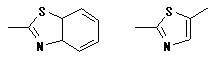
|
18. Polysulfones / sulfoxides / sulfonates / sulfoamides
Polymer including oxidation sulfur structures the following on main chain.
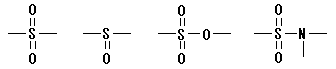
[Remarks]
- The above-mentioned structure includes it partially here of the ring structure.
|
19. Polyurethanes / thiourethanes
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (Xi shows either of O or S.)
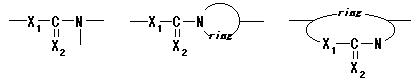 |
20. Polyureas / thioureas
Polymer including partial structures the following on main chain. (X shows
either of O or S.)
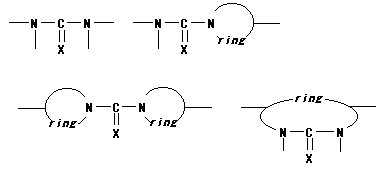
ex.) The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like
the above-mentioned.
 |
21. Polyvinyls
A main chain consists only of the aliphatic hydrocarbon radical, and is
polymer including either of the following in the side chain.
- Aromatic ring
- Radical that contains hetero atom (atoms other than C and H) and hetero
atoms.
However, when the halogen is contained as a hetero atom, it is limited
to the one of the following shape, and the one to take other bond forms
is classified only into Polyhalo-olefins.
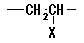 X = F, Cl, Br, I X = F, Cl, Br, I
[Remarks]
- The carbon atom of a main chain of prefered constituional unit (CU) is
not limited. (Do not limit the carbon atom of a main chain as two. )
- Polymer classified into Polystyrenes and Polyacrylics is classified into
Polyvinyls at the same time.
- Polyvinyls is not classified at the same time with Polyolefins and/or Polydienes.
- When double bond C=C and triple bond CC are included in a main chain, it
is classified into here.
|
22. Other polymers
The following one exists as an example of a partial structure like the
above-mentioned. |
|
|
CU chemical formula & formula weight |
|
Chemical formula of constituional unit (CU) of polymer.
The carbon and hydrogen are previously described and other elements are
alphabetical orders.
Moreover, the sum total of the atomic weight of each atom shown in CU chemical formula is called the amount of the expression.
ex.) Constitutional unit (CU) chemical structure
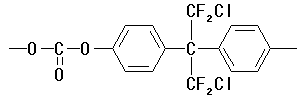
Chemical formula: C16H8Cl2F4O3
Formula weight: 395.14 |
|
|
|
First order structure |
|
In PoLyInfo, the data of the following item is adopted as a first order
structure.
The first order structure in PoLyInfo is a information when the Polymer
chain is seen within the range that is bigger than the unit of the composition
(repetition) targeted by the polymer dictionary,
- End radicals other than constitutional unit (CU) and information on chemical
structure in joint part.
- The arrangement of two or more constitutional unit(CU) and information
on chain.
It collects when the description is in the document of each sample that
adopts data assumed to be a data source about which item. |
|
Stereoregularity
Qualitative, quantitative, structural information on the tactisity and
the geometrical isomerism are collected.
Isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic are abbreviated with it-, st-, and
at-.
Trans-1,4-, cis-1,4- and 1,2- of polydiene are also collected to the stereoregularity.
Quantitative information is described in order of the content (item) and
measured values and the measuring method.
- ex.1) it-, pentad 0.985 by 13C-NMR
- ex.2) 1,4-cis 44%, 1,4-trans 42%, 1,2- 14% by IR
Stereo arrangement of R/S and D/L is collected here when it is information
for the chain of the constitutional unit. |
End-group and branch point (junction point)
The kind and the name are collected as information on the end radical and
the joint part.
The kind: The following is specified.
1. End group
2. Branching part
3. Junction part
4. Central part of star polymer
The name: The name of the end radical and the joint part as the description
in the document is collected. |
Other first-order structures
First order structures other than the above-mentioned are collected.
Moreover, information etc. are collected here concerning the optical isomer
in constitutional unit (CU).
The reason for this is that the polymer dictionary has been excluded the optical isomer. |
|
|
Average molecular weight |
|
Five kinds of the following are adopted as a Average molecular weight in
PoLyInfo.
- Number-average molecular weight (Mn)
- Weight-average molecular weight (Mw)
- z-average molecular weight (Mz)
- Viscosity-average molecular weight (Mv)
- GPC (SEC) peak molecular weight (Mp)
The following of the measuring method is specified.
- Gel permeation chromatography (GPC)
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Osmometry (Membrane osmometry)
- Vapor pressure osmometry (VPO)
- Cryoscopy
- Ebullioscopy
- Light scattering method (LS)
- Viscosity
- Others
|
|
Solution viscosity |
|
The data of the following item is gathered as a value that becomes the
standard of molecular weight.
Refer to a pertinent paragraph of the Propertiy item for Intrinsic viscosity
[eta]
- eta inh
- Reduced viscosity
- Specific viscosity (Relative viscosity increment), etc.
|
|
Melt flow rate (MFR) |
|
Amount of thermoplastic material pushed out under specific examination
condition in fixed time.
[Synonym]
Melt flow index (MFI)
Melt index (MI) |
|
Solvent / Non-solvent |
|
It is used respectively in the following meaning in PoLyInfo.
- Solvent: The solvent in which the polymer is soluble.
- Non-solvent: The solvent in which the polymer is not soluble.
|
|
Crystallographic information |
|
In PoLyInfo, the following information is adopted as information on the
crystal of the Polymer sample that adopts data.
- Crystallinity (degree of crystallization)
- Orientation
- Crystal type
- Crystal structural information
|
|
Processing information |
|
In PoLyInfo, the following information is collected on the molding method
and state after it molds as information on the Polymer sample that adopts
data.
- [Molding method]
The following is specified.
- Solvent casting
- Compression
- Blow (bottole)
- Extrusion
- Spinning
- Injection
- Calender (Roll)
- Spin casting (Spin coating)
- Blown film (Inflation film)
- Content shown in data sources other than the above-mentioned
- Molding conditions
- The temperature, pressure, time, and the solvent, etc. are collected.
[Treating method]
The following is specified.
- Annealing
- Quenching
- Stretching
- Crystallization
- As polymerized
- As received
- Thermal treatment
- Conditioning
- Content shown in data sources other than the above-mentioned
- Treating condition
The temperature, time, and the environment, etc. are collected.
ex.) (quenching) from the melt into ice water, (stretching) x5, RT, N2,
(annealing) 70C, 5h, in vacuo
[Sample shape]
The following is specified.
- Film
- Sheet
- Powder
- Pellet
- Fiber
- Block
- Single crystal
- Solution
- Disk
- Cylinder
- Plate
- Bar
- Bulk
- Content shown in data sources other than the above-mentioned
[Remarks]
Other information on molding and shape is described. Information on the
size of the molded sample is described here.
- (The thickness of film and sheet, and the diameter of the fiber etc. are
indicated.)
[State after molding]
The following is specified for a state after molding.
- Crystal
- Amorphous
- Content shown in data sources other than the above-mentioned
Crystalline and Semi-crystalline is being classified into Crystal when
Tm is observed.
|
|
|
Property |
|
property shown in the Property item list are collected in PoLyInfo. When the property name of the property item
list is clicked, the following explanation is shown about itself.
[Property item]
Definition and the explanation of property are shown. property enumerated
here are possible to be specified on "Polymer List".
[Unit]
The unit of property is displayed.
- Adopted unit
- Other units
- SI unit
[Measuring method]
The typical one of the measuring method is enumerated. The measuring method not listed here is collected if cited in the literature.
[Measurement standard]
The main measurement standards are enumerated. The measurement standard
not listed here is collected if cited in the literature.
[Measurement condition]
Indispensable measurement conditions are shown in measuring the property.
As a typical thing, there is temperature in the case of property with temperature
dependncy, heating and cooling rate in thermal character, and frequency
in the dynamic measurement etc. Also on the measurement conditions which
are not shown here, if described by the source of data, it will be recorded.
When itself is measured, an indispensable measurement condition is shown.
There are heating rate in a temperature and a thermal character for property
with the temperature dependency and a frequency in cooling rate and the
dynamic measurement, etc. assuming that it is typical.
[Notes]
Notes on each property item are shown.
[Related term]
It explains a synonym and a related word.
[Related information]
Accompanying item obtained at the measurement of itself is shown.
They are collected as much as possible if these information accompanies
the measurement data and it is described in the data source.
It shows in order referring in the round bracket when referring to definition
and the descriptions of < note > IUPAC, ISO・JIS, and other dictionaries,
etc.
|
|

