[Property item]
 Density: Density:
- Mass for each unit volume of material in t C.
- Specific volume: Reciprocal of density.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
g/cm3 |
| [Other units] |
1 lb/ft3 = 1.60185 E(01)kg/m3
1 lb/in3 = 2.76799 E(04)kg/m3
1 kg/m3 = 1E(-03)g/cm3 |
| [SI unit] |
kg/m3
g/cm3 |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1505-18 |
Standard Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-Gradient technique |
| ASTM D792-20 |
Standard Test Method for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative density)
of Plastics by Displacement |
| ISO 1183-3:1999 |
Methods for determining the density of non-cellular plastics - Part 3:
Gas pyknometer method |
| ISO 1675:1985 |
Plastics -- Liquid resins -- Determination of density by the pyknometer
method |
| JIS K 7112:1999(2018) |
Plastics--Method of determining the density and relative density of non-cellular
plastics: ISO 1183-3:1999 |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
Distinction (crystal/amorphous/overall/unknown) between crystal part and
non-is preconditions.
[Notes]
The density has the temperature dependency, and it is being provided by
JIS, "The density means the case of 23C".
When the density of the crystal calculated from the X-ray diffraction data
is described, it is described clearly that it is a calculation value in
the remarks column.
[Related terms]
- Apparent density
Apparent density: The value which excludes the mass due to the cubic measure
of the sample of the material which includes both parties of the air gap
of permeability and the impassability disposition which exist normally
in the material. (ISO and JIS)
- Bulk density
Apparent density such as powder, pellet and vulcanization.
- Specific gravity
Ratio of mass of fixed cubic measure of the substance for the water of
the same body product which even absolute relative importance you call,
in the same temperature.
- Lorentz-Lorenz equation (Density-Refractive Index relation)
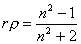
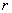 : Specific refactivity, : Specific refactivity, 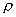 : Density, : Density, 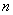 : Refractive index : Refractive index
|
[Property item]
 Refractive index: Refractive index:
- It is shown in ratio n (= c/v) of the sine of the angle of incidence and
the sine of angle of refraction, which equals to the ratio of speed (c)
of light in the vacuum (practically in the air) to speed (v) of light in
a transparent sample.
- [Unit]
- None
[Measuring method]
Abbe refractometer (Critical angle refraction method)
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1747-09(2019) |
Standard Test Method for Refractive Index of Viscous Materials |
| ISO 489:1999 |
Plastics -- Determination of refractive index |
| JIS K 7142:2014(2019) |
Determination of the refractive index of plastics: ISO 489 (1983) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the wavelength of light are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to describe clearly the wavelength of light (for instance,
a spectrum of sodium D line) and the temperature, because index of refraction
of a substance (n) has dependencies on them. It is noted as follows.
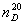
JIS is providing that it reports on the 3 column below the decimal point
as a value of the refractive index.
(Reference) Wavelength of the spectral lines utilized
| Wavelength (Å) |
Source |
Designation |
| 6562.79 |
Hydrogen (alpha line) |
C |
| 5892.62 |
Sodium (weighted mean of two lines) . |
D |
| 5460.74 |
Mercury |
e |
| 4861.33 |
Hydrogen (beta line) |
F |
| 4358.34 |
Mercury |
G |
[Related terms]
Dispersive poser (DP)
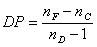
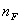 : refractive index at λ = 486.1 nm : refractive index at λ = 486.1 nm
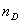 : refractive index at λ = 589.3 nm : refractive index at λ = 589.3 nm
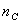 : refractive index at λ = 656.3 nm : refractive index at λ = 656.3 nm
Index of refraction --> Refractive index
Nonlinear refractive index coefficient 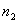
Definition: 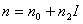 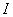 : Intensity of the beam : Intensity of the beam
Refractive index increments 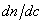 (refractive index increment) (refractive index increment)
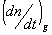 : Refractive index increment in state of the glass : Refractive index increment in state of the glass
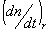 : Refractive index increment in state of rubber : Refractive index increment in state of rubber
|
Occurrence of the optical anisotropy which it occurs in the optical isotropic
body, is by stress and disappearance of the anisotropy with stress relief.
[Property item]
 Stress-optical coefficient: Stress-optical coefficient:
- During the alpha-relaxation regime and for small deformations, the birefringence
is proportional to the stress. This relation is quantified by the stress-optical
coefficient (SOC) or the ratio of birefringence to stress.
- Rt = Ct (p-q) = n λ
Here, C is a stress optical coefficient, t is thickness of the board ,
p, and q are main stress, n is a stripes number that passed a specific
point while adding the load, λ is a wavelength of light.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
1/GPa |
| [Other units] |
1cm2/dyn = 1(1/Pa)
1brewster = 1E(-12)(1/Pa) |
| [SI unit] |
1/Pa |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the wavelength of light are preconditions.
|
[Property item]
The following item is targeted as Crystallization kinetics in the data
adoption.
 R: Growth rate of crystal / spherulite: R: Growth rate of crystal / spherulite:
 k: Growth rate parameter of Avrami equation: k: Growth rate parameter of Avrami equation:
 n: Nucleation parameter of Avrami equation: n: Nucleation parameter of Avrami equation:
 Half-time of crystallization: (50% crystallization time) Half-time of crystallization: (50% crystallization time)
Tic: (Isothermal crystallization temperature)
- Avrami equation
-
- The expression that describes the speed of the crystallization, as follows,
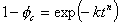 (1) (1)
here t and θc are time and a volume fraction of the generated crystals
respectively, at constant temperature. k and n are suitable parameters.
- Parameter k of expression (1) depends on the temperature.
- [Unit]
-
| R: Growth rate of crystal / spherulite |
[Adopted unit] |
nm/s |
| k: Growth rate parameter of Avrami equation |
[Adopted unit] |
None |
| n: Nucleation parameter of Avrami equation |
[Adopted unit] |
None |
|
| Half-time of crystallization |
| Time |
[Adopted unit] |
second |
Tic
|
[Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
|
[Notes]
The factor on spherulite growth speed (spherulitic growth rate) and on
nuclear generation speed (nucleation rate) includes many items, molecular
weight of the sample, the molecular weight distribution, and time, so on.
|
[Property item]
 Crystallization temperature: Crystallization temperature:
- Temperature when a part of whole of material perhaps changes from liquid
(unusual gas) or non-Jou solid into crystal condition.
 Heat of crystallization: Heat of crystallization:
- Calorie discharged when a part of whole of material perhaps changes from
liquid (unusual gas) or non-Jou solid into crystal condition.
- [Unit]
-
| Crystallization temperature |
Heat of crystallization |
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
[Adopted unit] |
cal/g |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Other units] |
kJ/kg |
| [SI unit] |
K |
[SI unit] |
kJ/kg (JIS) |
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA
[Measurement standard]
Crystallization temperature
| ISO 11357-3:2018 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 3: Determination
of temperature and enthalpy of melting and crystallization |
| JIS K 7121:2012(2017) |
Testing method for Transition Temperatures of Plastics: ADP ISO 3146:2000 |
Heat of crystallization
| ASTM D3418-15 |
Standard Test Method for Enthalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers
by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) |
| ISO 11357-3:2018 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 3: Determination
of temperature and enthalpy of melting and crystallization |
| JIS K 7122:2012(2017) |
Testing Method for Heat of Transition of Plastics |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate, Cooling rate, Heating, Cooling, from solution
[Notes]
This item name is vague the definition, and is too undesirable. It is because
the content shown whether "Crystallization" do intransitive verb
or transitive verb is different. Therefore, the crystallization temperature
at the time of cooling (Or, temperature rises) must be recorded with cooling
or the temperature rise speed.
In many cases, the crystallization cools melt quickly to the desired temperature,
and time and the speed to the crystallization in the temperature are measured.
(Isothermal crystallization) (Refer to Crystallization kinetics.)
|
[Property item]
 Glass transition temperature: Glass transition temperature:
- The middle point within the range of temperature where the glass metastasis
is done almost. (ISO)
The temperature at which polymer reversiblly change from viscous or rubbery
condition to hard and comparatively fragile condition, and vise versa.
The crystalline portion remains crystalline during the glass transition.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA, TMA, Dilatometry, Dielectric relaxation
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D3418-15 |
Standard Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Polymers By Thermal
Analysis |
| IEC 61006 Ed. 1.0:1991 (b) |
Method of test for the determination of the glass transition temperature
of electrical insulating materials |
| ISO 11357-1:2016 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 1: General
principles |
| ISO 11357-2:2020 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 2: Determination
of glass transition temperature |
| ISO 11359-2:1999 |
Plastics -- Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) -- Part 2: Determination of
linear thermal expansion coefficient and glass transition temperature |
| JIS K 7121:2012(2017) |
Testing method for Transition Temperatures of Plastics: ADP ISO 3146:2000 |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate, Frequency
[Notes]
The glass transition temperature changes remarkably depending on the test
conditions and on the examination method. (ISO)
Glass transition temperature Tg must depend on the observation time because
the glass transition can be understood as a kind of relaxation.
When Tg is obtained from the dynamic measurement, it is necessary to note
the measurement time scale.
[Related terms]
The following word is a synonym.
Glass temperature, Glass-rubber transition temperature, Glass transition
point
[Related information]
The following item that might be obtained along with the measurement of
the glass transition temperature is collected.
- Activation energy
- Transition Temperature
- Heat capacity increment (at Tg)
|
[Property item]
 Heat of fusion: Heat of fusion:
- The heat quantity which is required for changing the solid into the liquid
of the same temperature.
 Heat of fusion (mol conversion): Heat of fusion (mol conversion):
- The heat of fusion which is required for changing the solid every 1 mol.
However, "Mole" here is an amount of the expression of constituional
unit (CU).
- [Unit]
-
Heat of fusion
| [Adopted unit] |
kcal/g |
| [Other units] |
cal/g
kJ/kg
J/g |
| [SI unit] |
J/kg |
|
Heat of fusion (mol conversion)
| [Adopted unit] |
kcal/mol |
| [Other units] |
kJ/mol |
|
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D3418-15 |
Standard Test Method for Enthalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers
by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) |
| ISO 11357-3:2018 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 3: Determination
of temperature and enthalpy of melting and crystallization |
| JIS K 7122:2012(2017) |
Testing Method for Heat of Transition of Plastics |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate, Pressure
[Notes]
Whether the crystal section or the whole, value changes.
|
[Property item]
 Thermal decomposition temperature: Thermal decomposition temperature:
- The weight decrease rate in the temperature is collected with the temperature.
 Isothermal weight loss: Isothermal weight loss:
-
- Temperature
- Weight loss
- hours
- [Unit]
-
Thermal decomposition temperature
| Temperature |
[Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
| Weight loss |
[Adopted unit] |
% |
|
Isothermal weight loss
| Temperature |
[Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
| Weight loss |
[Adopted unit] |
% |
| Hours |
[Adopted unit] |
hour |
|
[Measuring method]
TG, Isothermogravimetric analysis
[Measurement standard]
| ISO 11358-1:2014 |
Plastics -- Thermogravimetry (TG) of polymers -- Part 1: General principles |
| ISO 11358-2:2014 |
Thermogravimetry (TG) of polymers -- Part 2: Determination of activation energy |
| ISO 11358-3:2013 |
Plastics -- Thermogravimetry (TG) of polymers -- Part 3: Determination of the activation energy
using the Ozawa-Friedman plot and analysis of the reaction kinetics |
| JIS K 7120:1987(2015) |
Testing Method of Plastics by Thermogravimetry |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate, gas, vacuum
[Notes]
"Heat decomposition temperature" is not specified clearly. The
"start temperature" of the heat weight measurement by TG, "middle
point temperature", "end temperature", etc. are prescribed
by ISO and JIS. JIS has also prescribed the reading of obtained TG curve
including the case of multi-stage mass reduction.
|
[Property item]
 LC Phase transition temperature: LC Phase transition temperature:
- Phase transition temperature of polymer liquid crystal.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA, Optical microscope, Dilatometry
[Measurement standard]
| ISO 3146:2000 |
Plastics -- Determination of melting behaviour (melting temperature or
melting range) of semi-crystalline polymers |
| JIS K 7121:2012(2017) |
Testing method for Transition Temperatures of Plastics: ADP ISO 3146:2000 |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate
|
[Property item]
 Linear expansion coefficient: Linear expansion coefficient:
- Reversible change in length of material for each length unit per one degree
temperature change. (ISO)
(Note) The value might change within the different range of the temperature.
 Volume expansion coefficient: Volume expansion coefficient:
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
[Measuring method]
Dilatometer, Pycnometer
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D696-16 |
Standard Test Method for Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion of Plastics
Between -30C and 30C With a Vitreous Silica Dilatometer |
| ASTM E228-17 |
Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials With
a Vitreous Silica Dilatometer: (general material) |
| ASTM E831-19 |
Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials by
Thermomechanical Analysis @m/m/C |
| ISO 11359-2:1999 |
Plastics -- Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) -- Part 2: Determination of
coefficient of linear thermal expansion coefficient and glass transition
temperature |
| JIS K 7197:2012(2017) |
Testing method for linear thermal expansion coefficient of plastics by
thermomechanical analysis |
[Measurement condition]
Temperature range (ex.). "below Tg"
State (ex.). "glassy, rubber"
[Notes]
αa, αb, and αc are separately described for the axis of the crystal.
A value different depending on the direction of the measurement is obtained
even by an anisotropic material.
The coefficient of thermal expansion is greatly different in lower than
Tg or upper than Tg. The applied range of the temperature is important.
[Related terms]
The coefficient of thermal expansion closely relates to the PVT relation.
- Reference such as PVT relation and Bulk modulus.
[related term ]
The coefficient of thermal expansion closely relates to the PVT relation.
- Reference such as PVT relation and * Bulk modulus.
|
[Property item]
 Melting temperature: Melting temperature:
- Temperature at which crystalline disappears by heating in semi-crystalline
material when measuring it under specific examination condition. (ISO,
JIS) Melting point is a synonym.
Equilibrium melting temperature
This is thermodynamically called a true melting point by the melting point
corresponding to the crystal of steady infinite thickness. Experimentally,
it is a temperature in the crystallization degree 100% at extrapolation
as for relate about crystallization degree-melting point.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
| [SI unit] |
K |
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA, TMA, Microscope
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D3418-15 |
Standard Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Polymers By Thermal
Analysis |
| ISO 11357-3:2018 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 3: Determination
of temperature and enthalpy of melting and crystallization |
| ISO 3146:2000 |
Plastics -- Determination of melting behaviour (melting temperature or
melting range) of semi-crystalline polymers by capillary tube and polarizing-microscope
methods |
| JIS K 7121 (1987) |
Testing method for Transition Temperatures of Plastics: ADP ISO 3146 (1985) |
[Measurement condition]
Heating rate, Frequency
|
[Property item]
 Specific heat capacity Cp: Specific heat capacity Cp:
- The heat needed for to raise the temperature one degree of the material
of the unit weight under the condition of constant pressure.
 Specific heat capacity Cv: Specific heat capacity Cv:
- The heat needed for to raise the temperature one degree of the material
of the unit weight under the condition of constant volume.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
cal/(g*C) |
| [Other units] |
kJ/(kg*K), J/(g*K) |
| [SI unit] |
J/(kg*K) |
[Measuring method]
DSC, DTA
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM E1269-11(2018) |
Standard Test Method for Determining Specific Heat Capacity by Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| ISO 11357-4:2014 |
Plastics -- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) -- Part 4:Determination
of specific heat capacity |
| JIS K 7123:2012(2017) |
Testing Method for Specific Heat Capacity of Plastics(Amendment 1) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
Heating rate.
[Notes]
In a fluorine hydrocarbon (PTFE etc.), "Heat capacity per carbon atom"
etc. might be shown.
|
[Property item]
 Thermal conductivity (of a homogeneous material not affected by thickness): Thermal conductivity (of a homogeneous material not affected by thickness):
- Speed of flow of heat in original of stationary state that passes area
of unit for each unit temperature inclination in vertical direction to
the area.
 Thermal diffusivity: Thermal diffusivity:
- Ratio of thermal conductivity of material to product of density and specific
heat of the material.
Rate of thermal diffusivity (α) and thermal conductivity (λ)
is in the relation of the following equation by using density (ρ) and
specific heat capacity (Cp).
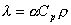
- [Unit]
-
| Thermal conductivity |
Thermal diffusivity |
| [Adopted unit] |
W/(m*K) |
[Adopted unit] |
m2/s |
| [Other units] |
cal/(m*K) |
[Other units] |
cm2/s |
| [SI unit] |
W/(m*K) |
[SI unit] |
m2/s |
[Measuring method]
Laser Flash, Opto-acoustic
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM C177-19 |
Standard Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal
Transmission Properties by Means of the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus |
| ASTM D5470-17 |
Standard Test Methods for Thermal Transmission Properties of Thin Thermally
Conductive Solid Electrical Insulation Materials |
| JIS A 1412-1:2016 |
Test method for thermal resistance and related properties of thermal insulations --
Part 1: Guarded hot plate apparatus |
| JIS A 1412-2:1999(2016) |
Test method for thermal resistance and related properties of thermal insulations --
Part 2: Heat flow meter apparatus |
| JIS A 1412-3:1999(2016) |
Test method for thermal resistance and related properties of thermal insulations --
Part 3: Circular pipe apparatus |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Notes]
Heating Method and Sample shape, etc. are shown.
|
[Property item]
 Dielectric constant, DC: Dielectric constant, DC:
- Relative permittivity measured in direct current.
 Dielectric breakdown voltage: Dielectric breakdown voltage:
- Voltage necessary to cause destructive electrical discharge between two
conductors.
Relative dielectric constant (relative permittivity)
The ratio for the capacitance between the identical arrangement electrode
in, in the vacuum of capacitance of the condenser where the space between
and around the electrode is filled up completely and monopolistically with
that insulating material.
Synonym: Relative permittivity
- [Unit]
-
| Dielectric constant (DC) |
None |
| Dielectric breakdown voltage |
[Adopted unit] |
kV/mm |
| [Other units] |
kV/mil |
[Measuring method]
Bridge, Step, Reflection, Digital
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D149-20 |
Standard Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength
of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Commercial Power Frequencies |
| ASTM D150-18 |
Standard Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric
Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation |
| ASTM D3755-20 |
Standard Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength
of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials Under Direct-Voltage Stress |
| JIS C 2110-1:2016 |
Solid electrical insulating materials -- Test methods for electric strength -- Part 1: Tests at power frequencies |
| JIS C 2110-2:2016 |
Solid electrical insulating materials -- Test methods for electric strength -- Part 2: Tests using direct voltage |
| JIS C 2110-3:2016 |
2016 Solid electrical insulating materials -- Test methods for electric strength -- Part 3: Tests using impulse voltage |
| JIS C 2151:2019 |
Testing methods of plastic films for electrical purposes |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement voltage are preconditions.
[Notes]
PoLyInfo use , as for Dielectric constant, specific dielectric constant
ε/εo (Permittivity of the polymer/permittivity of the vacuum)
[Related terms]
Dielectric breakdown strength (dielectric breakdown or more)
It is a minimum voltage in which the dielectric breakdown is caused when
the voltage is added to an electric insulating material. It is shown by
the ..exclusion.. value(potential gradient at the time of dielectric breakdown)
in the thickness of the break down voltage of the sample, and, in general,
it shows by the unit of kV/mm usually.
|
[Property item]
 Dielectric constant (AC), ε' (Storage dielectric constant) (storage permittivity) Dielectric constant (AC), ε' (Storage dielectric constant) (storage permittivity)
- Real part of complex permittivity.
 Dielectric loss factor, ε" (Loss dielectric constant) (loss permittivity) Dielectric loss factor, ε" (Loss dielectric constant) (loss permittivity)
- Imaginary part of complex permittivity.
 Dielectric loss tangent, tan δ, (Dielectric dissipation factor) (Dielectric dissipation
factor) Dielectric loss tangent, tan δ, (Dielectric dissipation factor) (Dielectric dissipation
factor)
- Tangent ε"/ε' in dielectric loss angle.
- [Unit]
- None for all.
[Measuring method]
Bridge, Step, Reflection, Digital
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D150-18 |
Standard Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric
Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation |
| JIS K 6911:2006(2016) |
Testing method for thermosetting plastics |
| JIS C 2151:2019 |
Method of examining plastic film for electricity |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement frequency are preconditions.
Besides, Heating rate, Cooling rate, and Gas, etc.
[Notes]
The permittivity originally has the unit of F/m (basic unit of SI). Generally,
the relative permittivity is called a permittivity. The term of JIS also
follows this. It is often measured with a low frequency, and, in this case,
the permittivity of the measurement is a real part of complex permittivity.
|
[Property item]
 Volume resistivity: Volume resistivity:
- The value obtained dividing the voltage inclination of the material by
the current.
(Note) In the metric system, the volume resistivity shown by ohm centimeter
of the material is equal to the volume resistance between surfaces face
to face of the material of 1cm cube.
 Surface resistivity: Surface resistivity:
- (Note) The surface resistivity of the material is equal to the surface
resistance of two interelectrode formed between the vicinity where one
square is opposite. The square size is not important.
- Electric conductivity:
A reciprocal of the electric resistance.
- [Unit]
-
| Volume resistivity |
[Adopted unit] |
Ω*cm |
| [Other units] |
MΩ*cm |
| Surface resistivity |
[Adopted unit] |
MΩ |
| [Other units] |
Ω |
| Electric conductivity |
[Adopted unit] |
1/(Ω*cm) |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D257-14 |
Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials |
| ISO 3915:1981 |
Plastics -- Measurement of resistivity of conductive plastics |
| JIS K 7194:1994(2016) |
Testing method for resistivity of conductive plastics with a four-point
probe array |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Related terms]
Specific resistivity (resistivity)
It is the same as surface resistance (Ω) or volume resistance (Ωcm).
|
[Property item]
 Gas permeability coefficient P: Gas permeability coefficient P:
 Gas diffusion coefficient D: Gas diffusion coefficient D:
- Constant that shows speed of diffusion in diffusion equation.
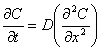
 Gas solubility coefficient S: Gas solubility coefficient S:
- [Unit]
-
Gas permeability coefficient P
| [Adopted unit] |
cm3(STP) cm/ (cm2*s*Pa) |
| [Other units] |
cm3(STP)cm/(cm2*s*cmHg)
cm3(STP)cm/(cm2*s*atm)
cm3(STP)cm/(cm2*24h*atm)
cm3(STP)cm/(cm2*24h*atm)
cm3(STP)cm/(cm2*24h*bar) |
| [SI unit] |
mol*m/(m2*s*Pa) |
|
Gas diffusion coefficient D
| [Adopted unit] |
cm2/s |
| [SI unit] |
m2/s |
Gas solubility coefficient S
| [Adopted unit] |
cm3(STP)/(cm3Pa) |
|
| (note) STP: Standard temperature and pressure = 273.15 K, 1.013*10E(05)
Pa |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1434-82(2015) |
Standard Test Method for Determining Gas Permeability Characteristics of
Plastic Film and Sheeting |
| ASTM D3985-17 |
Standard Test Method for Oxygen Gas Transmission Rate Through Plastic Film
and Sheeting Using a Coulometric Sensor |
| ISO 2556:1974 |
Plastics -- Determination of the gas transmission rate of films and thin
sheets under atmospheric pressure -- Manometric method |
| JIS K 7126-1:2006(2015) |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of gas-transmission rate-
Part 1 : Differential-pressure method |
| JIS K 7126-2:2006(2015) |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of gas-transmission rate-
Part 2 : Equal-pressure method |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
Permeant: The penetration gas kind (low molecular compound) is an indispensable
matter.
Additionally, RH(relative humidity), time, and pressure are needed.
[Notes]
Vapor coefficient of permeability is converted to the cubic measure of
the vapor of normal condition generally. In case of the water, because
in normal condition it is the liquid, the unit which is used in the literature
some kind of ones note is necessary.
[Related information]
The following item that might be obtained along with the measurement of
the gas transmission coefficient is collected if shown in the literature.
Pre-factor and activation energy
EP: Activation energy of permeation
ED: Activation energy of diffusion
Es (ΔH): Activation energy of solubility --> heat of dissolution
|
[Property item]
 Solubility parameter (of polymer): Solubility parameter (of polymer):
- The characteristic of Polymer used when the dissolubility to the solvent
with Polymer is forecast.
 Hansen parameter delta-p (polar component δp): Hansen parameter delta-p (polar component δp):
 Hansen parameter delta-d (dispersion component δd): Hansen parameter delta-d (dispersion component δd):
 Hansen parameter delta-h (hydrogen bonding component δh): Hansen parameter delta-h (hydrogen bonding component δh):
- Hansen parameter
- Expressed by three components of the above-mentioned to improve the accuracy
of Hildebrand parameter.
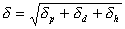
- Cohesive energy density, CED
- [Unit]
-
Solubility parameter (of polymer)
Hansen parameter delta-p (polar component δp)
Hansen parameter delta-d (dispersion component δd)
Hansen parameter delta-h (hydrogen bonding component δh) |
[Adopted unit] |
(J/cm3)1/2 |
| [Other units] |
(cal/cm3)1/2, (MPa)1/2 |
| [SI unit] |
(J/m3)1/2, (MPa)1/2 |
| Cohesive energy density, CED |
[Adopted unit] |
(cal/cm3) |
| [Other units] |
MPa |
[Measuring method]
Resilience, Solution viscosity, Swelling, Density measurement
[Measurement condition]
Test solvent names, temperature, and pressure
[Notes]
Polymer is often minute crosslinked when measuring it by the Swelling law.
In this case, obtained solution properties are handled assuming that there
is not a minute crosslinking for polymer structures.
[Related terms]
Hildebrand parameter
Solubility parameter
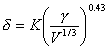
�: Solubility parameter and K:
Constant and γ Surface tension
Molar cohesion energy per monomeric unit
Molar cohesion energy per monomeric unit
Cohesion energy for each unit (≒CU) of monomer
SP value (SP value)
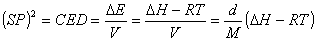
Here
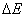 : Evaporation energy (cal/mol) : Evaporation energy (cal/mol)
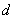 : Density (g/cc) : Density (g/cc)
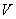 : Mole capacity (cc/mol) : Mole capacity (cc/mol)
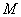 : Gram-molecular weight (g/mol) : Gram-molecular weight (g/mol)
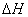 : Evaporation latent heat (cal/mol) : Evaporation latent heat (cal/mol)
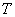 : Absolute temperature (K) : Absolute temperature (K)
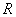 : Gas constant (1.987cal/(mol*K)) : Gas constant (1.987cal/(mol*K))
The SP value can be experimentally obtained for the solvent by the above-mentioned
expression, for polymers it is calculated from the expression of the following
Small because polymer is not volatile.
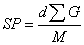
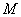 : Unit molecular weight of Polymer : Unit molecular weight of Polymer
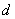 : Density : Density
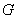 : Peculiar constant to atom group and radical : Peculiar constant to atom group and radical
|
[Property item]
 Interfacial tension: Interfacial tension:
- When two phases touch, the power which works in the boundary. If one phase
is the vapor, it is said the surface tension.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
mN/m |
| [Other units] |
dyn/cm |
| [SI unit] |
N/m |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1331-14 |
Standard Test Methods for Surface and Interfacial Tension of Solutions
of Surface-Active Agents |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Notes]
Partner polymer is shown in the remarks column.
|
[Property item]
 Surface tension: Surface tension:
- Work for each unit area necessary for changing surface area of material.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
mN/m |
| [Other units] |
dyn/cm |
| [SI unit] |
N/m |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Notes]
In case of critical surface tension, the effect is stated in the remarks column.
|
[Property item]
 Water absorption: Water absorption:
- Amount of moisture that material absorbs under specific examination condition.
- [Unit]
-
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D570-98(2008) |
Standard Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics |
| ISO 62:2008 |
Plastics-Determination of water absorption |
| JIS K 7114:2001(2020) |
Plastics-Method of test for the determination of the effects of immersion
in liquid chemicals. (ISO 175:1999) |
| JIS K 7209:2000(2019) |
Plastics-Determination pf water absorption. (ISO 62:1999) |
| JIS K 7223:1996(2016) |
Testing method for water absorption capacity of super absorbent polymers |
| JIS K 7224:1996(2016) |
Testing method for water absorption rate of super absorbent polymers |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
Other conditions, whether immersed in water or not, RH(relative humidity),
and Time, etc.
[Notes]
The state adjustment of the test piece before examination is provided for
in detail by JIS
[Related terms]
Moisture absorption
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller equation, BET equation
Expression of general moisuture absorption.
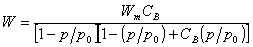
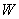 : mass of gas adsorbed (per mass of dry solid) : mass of gas adsorbed (per mass of dry solid)
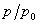 : relative pressure : relative pressure
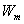 : mass of gas corresponging to monolayer coverage : mass of gas corresponging to monolayer coverage
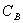 : constant which reflects the overall free energy of adsorption : constant which reflects the overall free energy of adsorption
|
[Property item]
 Water vapor transmission: Water vapor transmission:
- The quantity of the steam amount under provided temperature and humidity
conditions, which passes through unit area of film materials in fixed time.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
g*mil/(cm2*24h) |
| [Other units] |
g/(cm2*24h) |
(Note) g/(cm2*24h) is an amount of penetration for each unit area,
and g*mil/(cm2*24h) is the one that thickness (mil) was put on g/(cm2*24h).
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM E96/E96M-16 |
Standard Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Materials |
| ASTM D1653-13 |
Standard Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Organic Coating Films |
| ASTM D3833/D3833M-96(2019) |
Standard Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission of Pressure-Sensitive
Tapes |
| ASTM D7709-12(2017) |
Standard Test Methods for Measuring Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) of
Pharmaceutical Bottles and Blisters |
| ASTM F1249-20 |
Standard Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission Rate Through Plastic
Film and Sheeting Using a Modulated Infrared Sensor |
| JIS K 7129-1:2019 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 1: Humidity detection sensor method |
| JIS K 7129-2:2019 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 2: Infrared detection sensor method |
| JIS K 7129-3:2019 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 3: Electrolytic detection sensor method |
| JIS K 7129-4:2019 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 4: Gas-chromatographic detection sensor method |
| JIS K 7129-5:2016 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 5: Pressure sensor method |
| JIS K 7129-6:2016 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 6: Atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometer method |
| JIS K 7129-7:2016 |
Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of water vapour transmission rate-Part 7: Calcium corrosion method |
| JIS Z 0208:1976(2017) |
Testing Method for Determination of the Water Vapour Transmission Rate
of Moisture-Proof Packaging Materials (Dish Method) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
Besides, Immersed in water, RH(relative humidity), and Time, etc.
[Related terms]
Water vapor transmission rate
|
[Property item]
 Diffusion coefficient (of the polymer molecule): Diffusion coefficient (of the polymer molecule):
- Here, diffusion coefficients of the Polymer molecule are collected.
The diffusion coefficient of a low molecule and a gas into Polymer is Gas diffusion coefficient.
- [Unit]
-
[Measuring method]
- Light scattering method
- Ultracentrifugal methodOptical method
- Optical method
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement solvent are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to note no confusion with Gas diffusion coefficient.
It is necessary to evaluate it together with the data of molecular weight.
|
[Property item]
 Good solvent: Good solvent:
- Solvent with Θ temperature that is extremely lower than normal temperature.
 Poor solvent: Poor solvent:
- Solvent with Θ temperature in the vicinity of normal temperature.
- [Unit]
- None
[Notes]
The case to do handling that is more theoretical than solvent (Solvent names) /non-solvent (Non-solvent names) corresponds.
|
[Property item]
 Intrinsic viscosity: Intrinsic viscosity:
- Reduced viscosity in infinite dilute solution of the polymer or limit of
the value of of inherent viscosity.
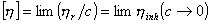
- [Unit]
-
[Measuring method]
Ubbelohde (Cannon-Ubbelohde)
Cannon-Fenske
Ostwald
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D2857-16 |
Standard Practice for Dilute Solution Viscosity of Polymers |
| ASTM D5225-17 |
Standard Test Method for Measuring Solution Viscosity of Polymers with
a Differential Viscometer |
| ASTM D445-19a |
Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque
Liquids (the Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity) |
| ISO 1628-1:2009/Amd 1:2012 |
Guidelines for the standardization of methods for the determination of
viscosity number and limiting viscosity number of polymers in dilute solution
- Part 1:General conditions
1628-2:2020: - Part 2: Poly (vinyl chloride) resins
1628-3:2010: - Part 3: Polyethylenes and polypropylenes
1628-4:1999: - Part 4: Polycarbonate (PC) moulding and extrusion materials
1628-5:1998: - Part 5: Poly (alkylene terephthalates)
1628-6:1990: - Part 6: Methyl methacrylate polymers |
There is no standard of a general viscosity measuring method in JIS. There
is a description in the examination method of an individual resin.
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement solvent are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to evaluate it together with the data of molecular weight.
[Related terms]
- Limiting viscosity number
It is synonymous with a intrinsic viscosity.
Also as for this term, Staudinger index is known in documents related to
the polymer.
- Reduced viscosity
Ratio ηr/c of increase ηr of relative viscosity against mass density c of polymerization body
It is necessary to specify the unit.
- Inherent viscosity
Ratio to mass density c of polymer of natural logarithm of relative viscosity.
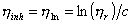
- Huggins equation
The expression that describes the substrate density dependency of Polymer
of reduction viscosity ηi/c for a thin Polymer solution
kH is Hagins coefficient here, and [η] is a intrinsic viscosity. (IUPAC)
- Mark-Houwink equation
(IUPAC) The expression that describes the molecular weight dependency of
a peculiar viscosity of Polymer.
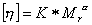
Mr is usually one of the molecular weight. (IUPAC)
Kuhn and Sakurada also did important contribution, and include their names
occasionally like Kuhn-Mark-Houwink-Sakurada equation occasionally.
|
[Property item]
 Radius of gyration: Radius of gyration:
- The parameter that characterizes the size of the particle regardless of
its shape.
It is defined in all the mass elements as a square root of the mass average
of ri2 for an rigid particle that consists of the mass element of in mass
that exists respectively in the distance of by the center of mass.
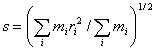
Take the average of all the conformational distribution for a non-rigid
particle.
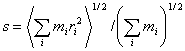
- [Unit]
-
[Measuring method]
LS (Light scattering method)
SANS (Small-angle neutron scattering)
SAXS (Small-angle X-ray scattering)
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement solvent are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to evaluate it together with the data of molecular weight.
It is necessary to note that it is easy to confuse the property with the
following terms.
- Unperturbed dimension
Extension of random coil of Polymer molecule of real existence that exists
in state of Sheeta.
Perturbed dimension
The extension of the random coil of the Polymer molecule of real existence
in the state of Sheeta.
End-to-end vector
The vector in which both ends of the linear polymer chain that reserves
a certain distribution seat are connected.
End-to-end distance
The length of the vector between one end to another end.
Though it is easy to make a mistake, Unperturbed dimension 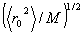 is a end-to-end distance above mentioned. is a end-to-end distance above mentioned.
|
[Property item]
 Second virial coefficient: Second virial coefficient:
-
- lWhen chemical potential μs of the solvent is developed with the power series of the solute of C in
the mass density, coefficient A2 of the next expression is meant the second virial coefficient.
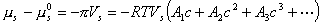
Here μs0 is chemical potential of the solvent in the standard condition of temperature
of system and by atmospheric pressure, as for osmotic pressure, and Vs. It is partial molar volume of the solvent.
- The following type that develops osmotic pressure as function of density
(Virial expansion) by showing gap from ideal solution of relation of Vant
Hoff,
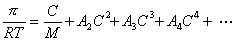
The coefficient A2 is called the second virial coefficient. The intermolecular effect of
two is shown.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
cm3*mol/g2 |
[Measuring method]
- Light scattering method (LS)
- Membrane osmosis
- Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- Sedimentation
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement solvent are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to note the dimension of the unit because some varieties
of the expressions are used.
There are a temperature dependency and a molecular weight dependency.
|
[Property item]
 sedimentation coefficient: sedimentation coefficient:
- To call the parameter which characterizes the movement of the particle
at the centrifugal force place, drift speed u per unit centrifugal acceleration.
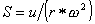
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
second |
| [Other units] |
1svedberg = 1E(-13)sec |
| [SI unit] |
second |
[Measuring method]
Ultra-centrifuge
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and the measurement solvent are preconditions.
[Notes]
It is necessary to evaluate it together with the data of molecular weight.
|
[Property item]
 Theta solvent, Θ solvent: Theta solvent, Θ solvent:
- See "Theta state".
 Theta-temperature, Θ temperature: Theta-temperature, Θ temperature:
- The temperature where the solution takes the state.
(Note) Theta state: Θ state
The state of the Polymer solution where the value of the second virial
coefficient becomes 0.
- The Polymer solution in the Θ state might look like the ideal solution,
and the Θ state is sometimes denoted as "pseudo-ideal state".
However, do not assume that the solution in the Θ state is the same
as the ideal solution.
- The solvent at this time is called "Theta solvent".
- [Unit]
-
| Theta solvent |
None |
| Theta-temperature |
[Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Measuring method]
- Cloud point (C.P.)
- Phase Equilibrium (PE)
- Diffusion coefficient-molar mass (DM)
- Sedimentation coefficient-molar mass (SM)
- Intrinsic viscosity-molar mass (VM)
|
[Property item]
 Dynamic viscosity Dynamic viscosity

Dynamic viscosity is defined in the same way as complex modulus (E*, G*).
The real part is the ratio of stress to strain rate of the same phase.


 :angular velocity
:angular velocity
 Dynamic viscosity
(Real part) Dynamic viscosity
(Real part)
 Dynamic viscosity
(Imaginary part) Dynamic viscosity
(Imaginary part)
 Loss tangent tan
Loss tangent tan
 ( = G'' / G' ) ( = G'' / G' )
[Unit]
| Dynamic viscosity |
[Adopted unit] |
N*s/m2 |
| [Other unit] |
Pa*s
dyn*s/cm2
poise |
[Measuring method
Rotational rheometer
[Measurement standard]
| ISO 6721-10:2015 |
Plastics -- Determination of dynamic mechanical properties
-- Part10: Complex shear viscosity using a parallel-plate oscillatory rheometer |
| JIS K 7244-10:2005 |
Plastics Determination of dynamic mechanical properties
Part10:Complex shear viscosity using a parallel-plate oscillatory rheometer |
[Measurement condition]
Temperature, Frequency |
[Property item]
 Melt viscosity
Viscosity of polymer in molten state Melt viscosity
Viscosity of polymer in molten state
[Unit]
| [Adopted unit] |
N*s/m2(= Pa*s) |
| [Other unit] |
dyn*s/cm2(= poise) |
| [SI Unit] |
Pa*s |
[Measuring method]
Capillary rheometer
Rotational rheometer
Brookfield type single and cylinder rotation viscosity meter and double
and cylinder rotation viscosity meter
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D5481-13(2020) |
Standard Test Method for Measuring Apparent Viscosity at High-Temperature
and High-Shear Rate by Multicell Capillary Viscometer |
| ISO 2555:2018 |
Plastics -- Resins in the liquid state or as emulsions or dispersions --
Determination of apparent viscosity using a single cylinder type rotational viscometer method |
| ISO 3219:1993 |
Plastics -- Polymers/resins in the liquid state or as emulsions or dispersions
-- Determination of viscosity using a rotational viscometer with defined
shear rate |
| ISO 11442:2006 |
Plastics -- Determination of fluidity of plastics using capillary and slit
-- die rheometers |
| ISO 12058-1(2018) |
Plastics -- Determination of viscosity using a falling-ball viscometer
-- Part 1: Inclined-tube method |
| JIS K 7117-1:1999(2018) |
Plastics--Resins in the liquid state or as emulsions or dispersions--Determination
of apparent viscosity by the Brookfield Test method(ISO 2555:1989) |
| JIS K 7117-2:1999(2018) |
Plastics--Polymers/Resins in the liquid state or as emulsions or dispersions--Determination of viscosity using a rotational viscometer with defined shear rate(ISO 3219:1993) |
| JIS K 7199:1999(2015) |
Plastics-Determination of the fluidity of plastics using capillary and
slit-die rheometers. |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition. |
[Property item]
 Storage modulus: Storage modulus:
- Real part of complex modulus.
 Loss modulus: Loss modulus:
- Imaginary part of complex modulus.
 Loss tangent: Loss tangent:
- Ratio of Loss modulus to storage modulus.
- [Unit]
-
| Storage modulus |
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
| Loss modulus |
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
| Loss tangent |
[Adopted unit] |
% |
[Measuring method]
- Tensile tester
- DMA (contain Vibron)
- Ultrasonic measurement
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D4065-12 |
Standard Practice for Determining and Reporting Dynamic Mechanical Properties
of Plastics |
| ISO 6721-1:2019 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 1:General principles:
= JIS K 7244-1:1998(2018) |
| ISO 6721-2:2019 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 2: Torsion-pendulum
method
= JIS K 7244-2:1998(2018) |
| ISO 6721-3:1994 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 3: Flexural
vibraton--Resonance-curve method
= JIS K 7244-3:1999(2020) |
| ISO 6721-4:2019 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 4:Tensile
vibration--Non-resonance method:
= JIS K 7244-4:1999(2020) |
| ISO 6721-5:2019 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 5: Flexural
vibration--Non-resonance method
= JIS K 7244-5:1999(2020) |
| ISO 6721-6:2019 |
Plastics -- Detemination of dynamic mechanical properties -- part 6: Shear
vibration--Non-resonance method
= JIS K 7244-65:1999(2020) |
| ISO 6721-7:2019 |
Plastics -- Determination of dynamic mechanical properties -- Part 7: Torsional
vibration -- Non-resonance method
|
| ISO 6721-8:2019 |
Plastics -- Determination of dynamic mechanical properties -- Part 8: Longitudinal
and shear vibration -- Wave-propagation method
|
| ISO 6721-9: 2019 |
Plastics -- Determination of dynamic mechanical properties -- Part 9: Tensile
vibration -- Sonic-pulse propagation method
|
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature and frequency are preconditions.
|
[Property item]
 Tensile modulus: Tensile modulus:
- The ratio of the tensile stress to strain within the tensile limit of proportionality.
 Tensile stress (strength) at break: Tensile stress (strength) at break:
- Tensile stress at moment that test piece destroyed.
 Tensile stress (strength) at yield: Tensile stress (strength) at yield:
- Tensile stress where an increase in expansion is admitted without an increase
in gaining the weight on stress-strain curve.
 Elongation at break: Elongation at break:
- The elongation which corresponds to tensile breaking strength.
 Elongation at yield: Elongation at yield:
- The elongation which corresponds to tensile yield strength.
 Fiber tensile modulus: Fiber tensile modulus:
 Fiber tensile strength (at break): Fiber tensile strength (at break):
 Fiber tensile elongation (at break): Fiber tensile elongation (at break):
- [Unit]
-
Tensile modulus
Tensile stress (strength) at break
Tensile stress (strength) at yield |
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
|
Elongation at break
Elongation at yield |
[Adopted unit] |
% |
Fiber tensile modulus
Fiber tensile strength (at break) |
[Adopted unit] |
g/denier |
| Fiber tensile elongation (at break) |
[Adopted unit] |
% |
|
[Measuring method]
Tensile tester
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D638-14 |
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics |
| ASTM D412-16 |
Standard Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Rubbers and
Thermoplastic Elastomers-Tension |
| ASTM D1708-18 |
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics By Use of Microtensile
Specimens |
| ASTM D882-18 |
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting |
| ASTM D2370-16 |
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Organic Coatings |
| ASTM D3822/D3822M-14(2020) |
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Single Textile Fibers |
| ISO 527-1:2019 |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 1: General principles
=JIS K 7161-1-14(2019) |
| ISO 527-2:2012 |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 2: Test conditions
for moulding and extrusion plastics
=JIS K 7161-2-14(2019) |
| ISO 527-3:2018 |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 3:Test conditions
for films and sheets =JIS K 7127-99 |
| ISO 527-4:1997 |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 4: Test conditions
for isotropic and orthotropic fibre-reinforced plastic composites =JIS K 7164-05 |
| ISO 527-5:1997 |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 5: Test conditions
for unidirectional fibre-reinforced plastic composites =JIS K 7165-08 |
| JIS K 7161-1:2014(2019) |
Plastics -- Determination
of tensile properties -- Part 1: General principles(ISO 527-1:2019) |
| JIS K 7161-2:2014(2019) |
Plastics -- Determination of tensile properties -- Part 2: Test conditions
for moulding and extrusion plastics(ISO 527-2:2012) |
| JIS K 7127:1999(2018) |
Plastics?Determination of tensile properties?Part 3 : Test conditions for films and sheets(ISO 527-3:2018) |
| JIS K 7164:2005(2020) |
Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 4:Test conditions for isotropic and orthotropic fibre-reinforced plastic composites(ISO 527-4:1997) |
| JIS K 7165:2008(2017) |
Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 5:Test conditions for unidirectional fibre-reinforced plastic composites(ISO 527-5:1997) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Shear stress (strength) at break Shear stress (strength) at break
Shear stress at the sample break
 Shear stress (strength) at yield Shear stress (strength) at yield
Shear stress at the sample yield
[Unit]
Sheer modulus
Shear stress (strength) at break
Shear stress (strength) at yield |
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other unit] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D732-17 |
Standard Test Method for Shear Strength of Plastics by Punch Tool |
| JIS K 7244-2:1998(2018) |
Determination of dynamic mechanical properties-Part2 : Torsion-pendulum method |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Flexural modulus: Flexural modulus:
- The ratio of the difference of stress (σ2 - σ1) by the difference of distortion (ε2 - ε1), where distortion of 2 points which are stipulated ε1= 0.0005, and ε2= 0.0025, the stress for each one σ1 and σ2 .
 Flexural stress (strength) at break: Flexural stress (strength) at break:
- The maximum bending stress that appears to test piece during the bending
test to breaking. (ISO, JIS)
 Flexural stress (strength) at yield: Flexural stress (strength) at yield:
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
[Measuring method]
Tensile tester
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D790-17 |
Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced
Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials |
| ISO 178:2019 |
Plastics -- Determination of flexural properties |
| JIS K 7171:2016 |
Plastics-Determination of flexural properties (ISO 178: 1993) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Compressive modulus: Compressive modulus:
- The ratio of the difference of stress (σ2 - σ1 ) by the difference of distortion (ε2 - ε1), where distortion of two points which are stipulated ε1 = 0.0005, and ε2 = 0.0025, the stress for each one σ1 and σ2 .
 Compressive stress (strength) at break: Compressive stress (strength) at break:
- The maximum compression stress supported in compression test by test piece.
(ISO, JIS)
 Compressive stress (strength) at yield: Compressive stress (strength) at yield:
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
[Measuring method]
Tensile tester, DMA
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D695-15 |
Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Plastics |
| ISO 604:2002 |
Plastics -- Determination of compressive properties |
| JIS K 7181:2011(2016) |
Plastics -- Determination of compressive properties (ISO 604:2002) |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Creep rupture strength Creep rupture strength
Stress to produce rupture in a fixed amount of time(hr).
 Creep rupture time Creep rupture time
Time from applying test load to specimen to breaking.
 Creep strain Creep strain
Strain caused by the applied stress during a creep test at any given time.
 Creep modulus Creep modulus
Ratio of stress to creep strain.
 Creep compliance Creep compliance
Ratio of creep strain to stress, reciprocal of elastic modulus.
 Creep recovery Creep recovery
Strain obtained by subtracting the strain after a predetermined time has passed after removing the load
from the strain immediately before removing the load.
[Unit]
Creep rupture strength
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
Creep rupture time
|
[Adopted unit] |
hour |
| [Other units] |
day
month
year |
Creep strain
|
[Adopted unit] |
% |
Creep modulus
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other units] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
Creep compliance
|
[Adopted unit] |
1/GPa |
| [Other units] |
1/MPa
cm2/kgf
cm2/dyn
1/psi |
Creep recovery
|
[Adopted unit] |
% |
[Measuring method] Tensile tester
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D2990-17 |
Standard Test Methods for Tensile, Compressive, and Flexural Creep and Creep-Rupture of Plastics |
| ISO 899-1:2017 |
Plastics -- Determination of creep behaviour -- Part 1: Tensile creep |
| ISO 899-2:2003 |
Plastics -- Determination of creep behaviour -- Part 2: Flexural creep by three-point loading |
| JIS K 7115:1999(2015) |
Plastics Determinaion of creep behaviour Part1 : Tensile creep |
| JIS K 7116:1999(2015) |
Plastics Determination of creep behaviour Part 2 : Flexural creep by three-point loading |
[Measurement condition] Temperature, time, stress, load are precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Brittleness temperature: Brittleness temperature:
- Temperature with 50% probability of test piece brittle fracture, examined
according to ISO 974 (JIS 7216).
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D746-20 |
Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers
by Impact |
| ASTM D1790-14 |
Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic Sheeting by
Impact |
| ISO 974:2000 |
Plastics -- Determination of the brittleness temperature by impact |
| JIS K 7216:1980(2015) |
Testing method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 Deflection temperature under load: Deflection temperature under load:
- The temperature at which the test piece bends fixed distance, under a specific
examination condition with a constant bend load.
(Note) The term called "heat deflection temperature" (HDT) should be avoided for this property.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D648-18 |
Standard Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics Under Flexural
Load in the Edgewise Position |
| ISO 75-1:2020 |
Plastics - Determination of temperature of deflection under load - Part
1: General test method |
| ISO 75-2:2013 |
Plastics - Determination of temperature of deflection under load - Part
2: Plastics and ebonite |
| ISO 75-3:2004 |
Plastics- Determination of temperature of deflection under load-Part
3: High-strength thermosetting laminates and long-fibre-reinforced plastics) |
| JIS K 7191-1:2015(2020) |
Plastics - Determination of temperature of deflection under load - Part
1: General test method (ISO 75-1:1993) |
| JIS K 7191-2:2015(2020) |
Plastics - Determination of temperature of deflection under load - Part
2: Plastics and ebonite (ISO 75-2:1993) |
| JIS K 7191-3:2007(2017) |
Plastics-Determination of temperature of deflection under load-Part 3:
High-strength thermosetting laminates and long-fibre-reinforced plastics
(ISO 75-3:1993) |
|
[Property item]
 Softening temperature: Softening temperature:
- Temperature at which material transforms specific amount when measuring
it under specific examination condition. (ISO, JIS)
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Measuring method]
- Resilience
- Passing light intensity measurement
- Fisher-John melting apparatus
- Fisher-John's melting point apparatus
[Measurement standard]
| ISO 11359-3:2019 |
Plastics -- Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) -- Part 3: Determination of
softening temperature |
| JIS K 7196:2012(2017) |
Testing method for softening temperature of thermoplastic film and sheeting
by thermomechanical analysis |
|
[Property item]
 Vicat softening temperature: Vicat softening temperature:
- Raise the medium at a constant speed while adding a prescribed load through
a needle shape indenter who vertically puts it on the test piece of the
heating bath or the heating aspect, and measure the temperature of the
heating medium when a needle shape indenter invades by 1mm.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other units] |
K, F |
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1525-17e1 |
Standard Test Method for Vicat Softening Temperature of Plastics |
| ISO 306:2013 |
Plastic-Thermoplastic materials - detemination of Vicat softening temperature
(VST) |
| JIS K 7206:2016 |
Plastic-Thermoplastic materials - detemination of Vicat softening temperature
(VST) (ISO 306:1994) |
|
[Property item]
 Charpy impact: Charpy impact:
- The ratio of absorbed energy (J) devided by the original cross-sectional
area of the notch of the specimen.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
kJ/m2 |
| [Other units] |
gf*cm/cm2 |
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D6110-18 |
Standard Test Methods for Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched
Specimens of Plastics |
| ISO 179-1:2010 |
Plastics -- Determination of Charpy impact properties -- Part 1: Non-instrumented
impact test |
| ISO 179-2:2020 |
Plastics -- Determination of Charpy impact properties -- Part 2: Instrumented
impact test |
| JIS K 7077:1991(2016) |
Testing method for Charpy impact strength of carbon fiber reinforced plastics |
| JIS K 7111-1:2012(2017) |
Plastics-Determination of Charpy impact properties-Part 1: Non-instrumented impact test |
| JIS K 7111-2:2022(2017) |
Plastics-Determination of Charpy impact properties-Part 2: Instrumented impact test |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Measurement condition]
ISO 179 methods are used and results reported based on the cross-sectional
area at the notch (J/m2).
|
[Property item]
 Izod impact: Izod impact:
- The value of Absorbed energy (J) per unit of specimen thickness (m) at
the notch. (ASTM)
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
kJ/m |
| [Other units] |
kgf*cm/cm
lbf*ft/in |
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D256-10(2018) |
Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics |
| JIS K 7110:1999(2018) |
Plastics?Determinaion of Izod impact strength |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
[Notes]
The test method utilized here is ASTM D256.
The result of the Izod test is reported in energy lost (ft-lb or J) per unit of specimen thickness (cm or in) at the
notch.
These test methods resemble ISO 180:1993 in regard to title only.
The contents are significantly different.
ISO 180 methods are also used and results reported based only on the cross-sectional
area at the notch (J/m2).
|
[Property item]
 Rockwell hardness: Rockwell hardness:
- The value which was calculated from difference h of invasion depth of the
indenter in before and after the load test, including the standard load
first, test loaded, then next again resetting to the standard load.
- [Unit]
-
| [Adopted unit] |
The hardness scale is shown. E-, L-, M-, R- |
(Note) Scale
A scale in the Rockwell hardness is a peculiar sign to the combination
of indenter's kind, the test force, and the hardness calculation type installed.
[Measuring method]
Rockwell (load = 10kgf)
Rockwell superficial (load = 3kg)
[Measurement standard]
Hardness scale of ASTM and JIS(ISO)
| Scale |
Preliminary test force |
Test force |
Diameter mm of indenter |
Sign of JIS |
| R |
98N (10kgf) |
588N(60kgf) |
12.5 |
HRR |
| L |
588N(60kgf) |
6.25 |
HRL |
| M |
980N(100kgf) |
6.25 |
HRM |
| E |
980N(100kgf) |
3.13 |
- |
| K |
1470N(150kgf) |
3.13 |
- |
| α |
588N(60kgf) |
12.5 |
- |
| ASTM D785-08(2015) |
Standard Test Method for Rockwell Hardness of Plastics and Electrical Insulating
Materials |
| ISO 2039-2:1987 |
Plastics -- Determination of hardness -- Part 2: Rockwell hardness |
| JIS K 7202-2:2001(2015) |
Plastics -- Determination of hardness -- Part 2: Rockwell hardness (ISO
2039-2: 1987 ) |
|
[Property item]
 Shore hardness: Shore hardness:
- The measure with optional hardness that the plug depth of the specific
pushing needle pushed in into material is measured under the conditions
specified as ISO 868.
- [Unit]
- None
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D1415-18 |
Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-International Hardness |
| ASTM D2240-15e1 |
Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-Durometer Hardness |
| ISO 868:2003 |
Plastics -- Determination of indentation hardness by means of a durometer
(Shore hardness) |
| JIS K 7215:1986(2015) |
Testing method for Durometer Hardness of Plastics |
[Notes]
A genuine item is "Indentation hardness by Durometer" provided
for by ASTM D 785, ISO 868 or JIS K 7215, and not "Shore hardness"
that measures repulsive hardness.
|
[Property item]
 Oxygen index Oxygen index
- Minimum oxygen concentration(vol%) required for the sample to maintain flame combustion
in a mixed gas of oxygen and nitrogen.
- [Unit]
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D2863-19 |
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of Plastics (Oxygen Index) |
| ISO 4589-1:2017 |
Plastics -Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index -Part 1: General requirements |
| ISO 4589-2:2017 |
Plastics -Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index -Part 2: Ambient-temperature test |
| ISO 4589-3:2017 |
Plastics -Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index -Part 3: Elevated-temperature test |
| JIS K 7201-1:1999(2016) |
Plastics-Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index-Part1: Guidance |
| JIS K 7201-1:2007(2016) |
Plastics-Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index-Part2: Ambient-temperature test |
| JIS K 7201-1:2008(2017) |
Plastics-Determination of burning behaviour by oxygen index-Part3: Elevated-temperature test |
[Measurement condition]
The measurement temperature is a precondition.
|
[Property item]
 UL Flammability rating UL Flammability rating
Shows the degree of incombustibility in flammability tests on equipment and component materials
Established by US Underwriters Laboratories Limited Liability Company
[Unit]
UL Flammability rating 94V
| [Adopted unit] |
V-0
V-1
V-2
|
UL Flammability rating 94HB
| [Adopted unit] |
HB |
UL Flammability rating 94VTM
| [Adopted unit] |
VTM-0
VTM-1
VTM-2
|
[Measuring method] UL94
[Measurement standard]
| ASTM D3801-20 |
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Comparative Burning Characteristics of Solid Plastics in a Vertical Position |
| ASTM D635-18 |
Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position |
| ASTM D4804-20 |
Standard Test Method for Determining the Flammability Characteristics of Nonrigid Solid Plastics |
|
[Property item]
 ULTemperature Index
ULTemperature Index
Standards for long-term physical property evaluation of plastics materials
Established by US Underwriters Laboratories Limited Liability Company
[Unit]
ULTemperature Index
| [Adopted unit] |
C |
[Measuring method] UL
[Measurement standard]
| UL746B |
Standard for Polymeric Materials : Long Term Property Evaluations |
[Measurement condition]
Properties to measure
l;Tensile stress at break 2;Tensile stress at yield 3;Elongation 4;Impact strength 5;Write in
Elapse time
|
[Property item]
 Bulk modulus Bulk modulus
The value obtained by dividing the hydrostatic pressure (P) by the volume compression (?).(ISO,JIS)
 Compressibility Compressibility
Reciprocal of bulk modulus
 Zero pressure volume Zero pressure volume
Volume when pressure is extrapolated to zero
 Bulk modulus at zero pressure Bulk modulus at zero pressure
Compressibility when pressure is extrapolated to zero
[Unit]
Bulkmodulus
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other unit] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
Compressibility
|
[Adopted unit] |
1/GPa |
| [Other unit] |
1/MPa
cm2/kgf
cm2/dyn
1/psi |
Zero pressure volume
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other unit] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
Bulk modulus at zero pressure
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other unit] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
[Measuring method]1.PVT machine(Zolar), 2.IKV machine, 3.write in
Other measuring method
high pressure volume dilatometry ;
A.Measurement method of P-V-T at low pressure
Immersion method (wet method)
a. Floating and sinking method
b. Density gradient tube method
c. Water displacement method (libra method)
d. Pycnometer method
Gas replacement method (dry method)
e. Constant volume expansion method
B.Measurement method ofP-V-T at high pressure
a. Glass piezometer method (dilatometer method)
b. Piston displacement method
c. Bellows method (including Zoller)
[Measurement condition]
Temperature
|
[Property item]
 G valueValues used to indicate radiochemical yields G valueValues used to indicate radiochemical yields
Number of molecular changes per 100 eV of absorbed energy
Radiochemical yield G(X):Yield of radicals, various gasaseous products, cross-links, etc. generated by irradiation.
G(X)=n(X)/E (mol/J)
n(X):Amount of object (or event) X
E:energy (J)
G=1 (event/100eV) = 1.036ラ10-7 (mol/J)
[Unit]
| G value |
[Adopted unit] |
events/100eV |
[Measuring method]
[Measurement standard]
[Measurement condition]
Dose rate, Radiation source.
Atmosphere, Temperature.
|
[Property item]
 Pressure Pressure
 SpecificVolume SpecificVolume
 Temperature Temperature
[Unit]
Pressure
|
[Adopted unit] |
GPa |
| [Other unit] |
MPa
kgf/cm2
dyn/cm2
psi |
Specific volume
|
[Adopted unit] |
cm3/g |
Temperature
|
[Adopted unit] |
C |
| [Other unit] |
K
F |
[Measuring method]1.PVT machine(Zolar), 2.IKV machine, 3.??
Other measuring method
high pressure volume dilatometry ;
A.Measurement method of P-V-T at low pressure
Immersion method (wet method)
a. Floating and sinking method
b. Density gradient tube method
c. Water displacement method (libra method)
d. Pycnometer method
Gas replacement method (dry method)
e. Constant volume expansion method
B.Measurement method ofP-V-T at high pressure
a. Glass piezometer method (dilatometer method)
b. Piston displacement method
c. Bellows method (including Zoller)
|
[Property item]
 Half-value dose Half-value dose
Absorbed radiation amount that halves the physical property value
Irradiation dose rate: The number of photons, electrons, and ions given to a unit
space in a unit time. Expressed in roentgen / time (r / s, etc.).
Absorbed dose rate; the amount of energy absorbed per unit weight per unit time.
Expressed in rad / time (rad / s, rad / min, rad / h), etc.
hal-value period: Time until the radioactivity of radioactive substances is halved.
[Unit]
| Half-value dose |
[Adopted unit] |
Mrad |
| [Other unit] |
J/kg
Gy |
1rad = 1e-2 Gy
1J/kg = 1Gy = 100rad = 1e4erg/g
[Measurement condition]
The target physical properties are preconditions.
1;Tensile stress at break, 2;Tensile stress at yield, 3;Elongation, 4;Impact strength, 5;Write in
Temperature |
|

